What is a Hot Potato Voice or muffled voice that is seen in Peritonsillar Abscess? Tody’s topic is all about Hot Potato Voice or Hot Potato Speech: Introduction, Synonyms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment.
Hot Potato Voice or Hot Potato Speech
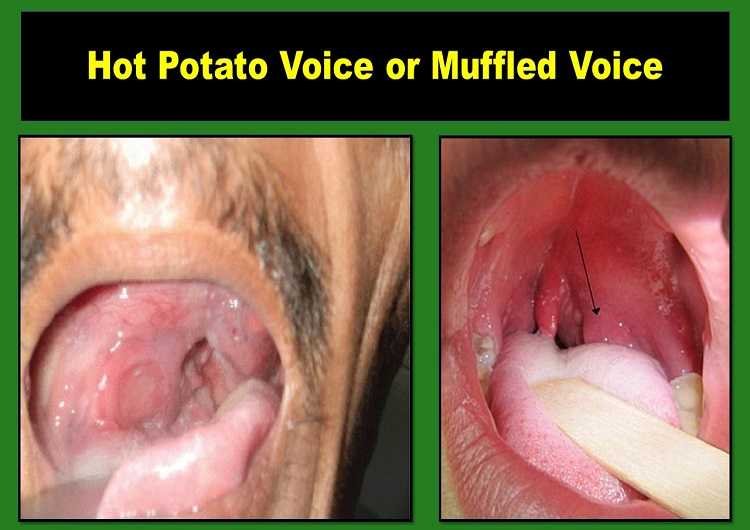
Hot potato speech, also known as hot potato voice or muffled voice, is pathognomonic of quinsy. It is a medical term, although a misnomer, for distortion or defect in resonance and quality of voice or sound.
In hot potato voice (HPV), the speech has muffled quality, characteristically comparable to a voice produced by a person with a very hot potato in his mouth.
According to The Free Medical Dictionary, “Hot Potato Voice is a term for a defect of resonance in which the speech has a muffled quality, fancifully likened to a person speaking with a hot potato in the mouth.
Etiology: Space-occupying lesions, e.g., lymphoid masses, quinsy—peritonsillar—cellulitis or abscess, tumors of the vallecula between the epiglottis and the base of the tongue”
Synonyms
- Hot potato speech
- Potato in mouth
Important MCQ
‘Hot potato’ voice is characteristically seen in which space infection?
- Retropharyngeal space infection
- Pterygomandibular space infection
- Lateral pharyngeal space infection
- Pre tracheal space infection
To know the answer to this question, keep reading the following notes about the hot potato sound.
A case study of a man with an HPV and neck swelling
By M Irfan and A Puvan Arul
Case history
A man in his late forties came with the complaint of painless left neck swelling for around 4 weeks. He noticed a change in his voice (thick, muffled voice, hot potato speech) 7 days before the onset of the symptoms.
Sore throat and odynophagia were other noticeable symptoms. He didn’t present any symptoms of fever, dysphagia, loss of weight, loss of appetite, or trismus, and there was no history of foreign body in the throat.
Examination and Provisional Diagnosis
Upon examination of the oral cavity, the following abnormalities were seen:
- An enlarged left tonsil occupies more than half of the oropharyngeal space, with a small residual airway.
The provisional diagnosis of this case with hot potato speech is lymphoma.
Hot potato voice causes
The “hot potato voice” is widely recognized as a symptom of peritonsillar cellulitis or abscess. Hot potato speech causes include acute epiglottitis, epiglottic abscess, meningioma (rarely), and others (unknown)
If the cause of a muffled voice is an epiglottic abscess, the patient will have a mild hot potato sound. Tender cervical lymphadenopathy may be present either unilaterally or bilaterally.
A patient with acute epiglottitis will have a muffled voice and the patient often complain of being tired and feeling lethargic due to their labored breathing.
Meningioma presenting as an oropharyngeal mass- an unusual presentation has also been found in the literature.
Is hot potato voice in peritonsilitis a misnomer?
Upon examination of the vocal tract in peritonsilitis, it is found that the hot potato speech is due to dyskinesis of the peritonsillar musculature.
But the muffled speech in people with a hot potato in their mouth is due to the interference in the movement of the anterior tongue. Thus, the changes in the vocal tract differ in these two cases and the title “hot potato voice” in peritonsillitis is a misnomer.
Mechanism of Hot Potato Speech
Hot potato voice is the result of an underlying transient velopharyngeal insufficiency combined with muffled oral resonance. It is classically described for peritonsillar abscess or cellulitis.
The main causes of hot potato voice are already explained. However, it can result from any space-occupying lesions. Frequently seen space-occupying lesions are given below.
- Lymphoid masses
- Quinsy – peritonsillar cellulitis or abscess
- Epiglottitis
- Tumors of vallecula between the epiglottis and the base of the tongue
- Lingual thyroid gland
- Foreign body
In a study, Discrimination of “hot potato voice” caused by upper airway obstruction utilizing a support vector machine, S Fujimura, et al. analyzed changes in the voice spectral envelope caused by upper airway obstructions by using a hybrid time-frequency model of articulatory speech synthesis.
They concluded that HPV caused by upper airway obstruction has a highly characteristic spectral envelope. Based on this distinctive voice feature, the SVM classifier, which was trained using synthetic data, was able to diagnose upper‐airway obstructions with a high degree of accuracy.
Diagnosis
If the cause of the hot potato speech is a peritonsillar abscess, the doctor will first perform an examination of your mouth and throat. They may take a throat culture or a blood test to diagnose your condition. Signs of an abscess include:
- swelling on one side of the throat
- swelling on the roof of the mouth
- redness and swelling of the throat and neck
Lymph nodes are often enlarged on the same side.
CT scans or MRIs are performed to see the abscess more closely. The doctor might also use a needle to draw fluid from the abscess. This fluid will be tested to check if there is an infection.
Treatment of Hot Potato Speech
The treatment of HPV depends upon the underlying cause of the space-occupying lesion. Antibiotics are the most common form of treatment for peritonsillar abscesses. Your doctor may also drain the pus in the abscess to accelerate healing. This is done by lancing (or cutting) the abscess to release fluids. Your doctor may also use a needle.
If you are unable to eat or drink, you may have to receive fluids for hydration intravenously (through an IV). You may need to take painkillers if you are experiencing a lot of pain.
Watch the video and listen how the hot potato really sounds like
The video on hot potato speech by Larry Mellick
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE Cushing Triad in ICP and Beck’s Triad
Sources
- Frantz TD, Rasgon BM. Acute epiglottitis: changing epidemiologic patterns. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;109:457-60.
- The American Society of Radiologic Technologists, 15000 Central Ave. SE, Albuquerque, NM 87123-3917.
- Uchibori M, Odake G, Ueda S, et al. Parapharyngeal meningioma extending from the intracranial space. Neuroradiology 1990; 32(1): 53-55.
- Thompson LD, Gyure KA. Extracranial sinonasal tract meningiomas: a clinicopathologic study of 30 cases with a review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24: 640-650.
- Weinberger JM, Birt BD, Lewis AJ, et al. Primary meningioma of the nasopharynx: case report and review of ectopic meningioma. J Otolaryngol 1985; 14: 317-322.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16360301/
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Rings in Eyes (Ophthalmology): Cholesterol, Blue, & More
Carpal Bones Mnemonic: Wrist Bones Names in Order
Cushing’s Triad in ICP: Pathophysiology, Mnemonic, & More
Acronym for Cranial Nerves Mnemonic – Dirty, Funny Tricks


